
Book a Consultation
Thank you!
Your form has been sent successfully.

Breast cancer is the uncontrolled growth of cells lining the breast’s ducts or lobules, and may start in one or both breasts. Most cases occur in women, but men can also be diagnosed.
The breast has three main parts: lobules that produce milk, ducts that carry milk to the nipples, and supporting tissue made up of fatty and fibrous material.
Cancer usually begins in the ducts or lobules and, if untreated, can spread through the blood and lymph vessels to other parts of the body.

Breast cancers are named based on the type of cells involved. The two broad categories are noninvasive and invasive breast cancers.
Noninvasive means cancer cells remain in the ducts or lobules where they started, without spreading into nearby tissue. This form usually grows slowly and is called ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS).
Most breast cancers, however, are invasive. These cancers break through normal breast tissue and can spread to nearby lymph nodes or other organs.
Invasive breast cancers usually grow faster and are considered more aggressive than noninvasive forms. The different types include:
• Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC) : IDC starts in a milk duct and spreads into the surrounding breast tissue. This is the most common form of breast cancer and may spread to other areas of the body if not treated.
• Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC): Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) begins in milk-producing lobules and often spreads into nearby breast tissue. ILC can be harder to detect on mammograms compared to invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) and carries a slightly higher risk of occurring in both breasts, although most cases affect only one.
• Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC): Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) is rare and aggressive. It usually begins as invasive ductal carcinoma in milk ducts and quickly spreads, causing redness, swelling, and skin changes.
• Paget disease of the breast: Paget disease is a rare breast cancer affecting the nipple area, causing flaky or irritated skin. It often occurs along with another type of breast cancer.
• Metaplastic breast cancer: Metaplastic breast cancer is very rare, aggressive, and difficult to treat. It can spread rapidly to other parts of the body and tends to have a less favorable outlook compared to other breast cancers.
Breast cancer symptoms vary by person, but the most common is a lump in the breast or underarm. Not all lumps mean cancer, but your doctor should check any new lump.
Other symptoms include:
You should also look out for these skin changes:
These signs can have non-cancerous causes, but it's always best to see your doctor promptly to determine the reason.
After an initial screening raises concerns, your primary care doctor may refer you to a breast cancer specialist for further tests. Specialized imaging is used to learn more about the breast changes seen during screening.
Mammograms, ultrasounds, and breast MRI each offer a different way to examine breast tissue closely.
•
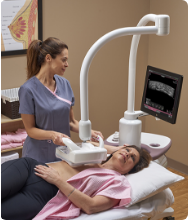
Mammograms: These are the main screening tool for early detection. They identify changes, such as microcalcifications, that could indicate early cancer. However, a biopsy is required to confirm a diagnosis.

•
Breast ultrasounds: This is a safe, painless test using sound waves to create images of breast tissue. It helps differentiate fluid-filled cysts from solid masses that mammograms may not clearly identify.
•
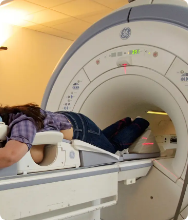
Breast MRI: This procedure uses strong magnetic and radio waves to take multiple detailed pictures of the inside of the breast on a computer. It helps determine the size and number of tumors inside the breast.
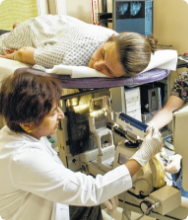
If imaging finds something suspicious, a biopsy is performed to obtain tissue samples for closer examination.
Your breast cancer doctor numbs the area to take a sample of breast tissue or fluid, which is later investigated under a microscope to establish the nature of the disease.
Breast cancer treatments fall into two main categories: local and systemic.

Local treatments directly target the tumor in the breast, without affecting the rest of the body. Surgery and radiation therapy are typical local treatments.
Breast-conserving surgery (also called lumpectomy, quadrantectomy, partial mastectomy, or segmental mastectomy) removes cancerous tissue from the breast, leaving the rest of the breast intact.
A mastectomy removes the entire breast, and sometimes both breasts (a double mastectomy).
Surgeons also check nearby lymph nodes to determine if cancer has spread. For some patients with small, low-risk Stage 1 cancers, surgery alone may be sufficient
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays or particles to destroy cancer cells that may remain after surgery.
The two main forms are external beam radiation, which delivers radiation from outside your body, and internal radiation (brachytherapy), which places radioactive material directly into the breast.
Treatment for Stage 2 breast cancer typically includes surgery, often combined with radiation or systemic therapy.
Systemic treatments use medicines that travel through the bloodstream to target cancer cells wherever they might be in the body. Doctors select treatments based on your cancer’s type, size, location, and stage.
• Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs that travel through the bloodstream to destroy cancer cells. These medicines are given intravenously or taken orally and reach cancer cells throughout the body.
• Hormone therapy: Hormone therapy is used for breast cancers that have hormone receptors, such as estrogen or progesterone. The therapy works by blocking these hormones or reducing their production, slowing or stopping cancer growth.
• Targeted drug therapy: Targeted therapy focuses on specific proteins that help cancer cells grow. These treatments block or disrupt these proteins, slowing or stopping the spread of cancer cells.
• Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy helps your immune system recognize and destroy cancer cells. It makes cancer cells easier for your immune system to identify, boosting your body's natural defenses.
Stage 4 breast cancer (metastatic breast cancer) has spread to distant parts of the body. Treatment usually includes a combination of systemic therapies (such as chemotherapy, hormone therapy, targeted therapy, or immunotherapy).
Surgery or radiation might be used to relieve symptoms or manage specific problems.
If you are looking for experienced breast cancer doctors in Florida, then speak to experts at ACTC.
The breast cancer oncologists at ACTC are dedicated to providing exceptional patient care and prescribing effective, personalized, and evidence-based treatment plans for their patients.
We're dedicated to supporting patients and their families at every step of their cancer journey, backed by a highly skilled team of breast cancer specialists
At ACTC, you can consult with our specialists:

Hematology/Oncology

Hematology/Oncology

Radiation Oncology
We provide comprehensive treatment for all forms of breast cancer at ACTC, including screening, diagnosis, staging, treatment, and long-term follow-up, in one convenient location.
Our team is committed to providing compassionate, personalized support for patients and families at every stage of their cancer journey.
Call 352-345-4565 or book an appointment

If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with breast cancer and are looking for treatment options, a random internet search for breast cancer center near me may not be the best option. Ensure you discuss treatment options with your primary care provider, who can in turn refer you to ACTC.
As one of Florida's leading breast cancer centers, we understand how a cancer diagnosis and treatment impact a person's physical and emotional well-being. Therefore, we work hard to make patients and their families feel secure. We provide comprehensive treatment for all forms of breast cancer at ACTC, including screening, diagnosis, staging, treatment, and long-term follow-up, all in one convenient location. Our breast cancer doctors are backed up by qualified clinical staff with over two decades of experience and a reputation for providing personalized treatment.
Schedule a consultation by calling
 352-345-4565
352-345-4565
Early warning signs include a new lump in the breast or armpit areas, itching, sudden increase in size or shape of breast, flaky skin, or change in color of breasts.
Risk factors for breast cancer include inherited genetic mutation (BRCA gene), family history, race and ethnicity, previous history of breast cancer, never having children, and having dense breasts.
According to the American Cancer Society, non-cancerous conditions produce similar signs and require investigations to rule out malignant tumors. The benign conditions that can be mistaken as breast cancer are - Ductal lobular hyperplasia, Lobular carcinoma in situ, Adenosis, Fibroadenoma, Phyllodes tumor, Intraductal papillomas, Fat necrosis and oil cysts, Mastitis, Duct Ectasia.
If you are based in (or near) Florida, you can schedule a consultation with an ACTC cancer specialist by calling 352-345-4565 or by completing the online form here. (we can provide a link to the form here)
Schedule a consultation by calling
 352-345-4565
352-345-4565